9/12/14
We continue learning about microbial metabolism.
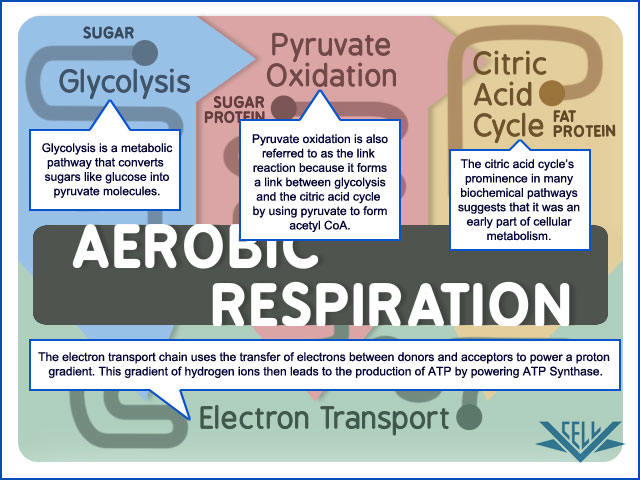
Cellular respiration is process cells use to convert E in chemical bonds of nutrients to ATP E.
Aerobic respiration
-involves an electron transport system
-final electron acceptor is oxygen gas.
-total theoretical maximum number atp generated perglucose in prokaryote is 38.In eukaryotr is 36-38.This different from prokaryote because depending on how 2NADH generated in cytoplasm during glycolysis enter mitochondria resulting 2 or 3 atp per NADH but in prokaryote there are no mitochondria 38 can be produce.
metabolic pathways-
We continue learning about microbial metabolism.
Cellular respiration is process cells use to convert E in chemical bonds of nutrients to ATP E.
Aerobic respiration
-involves an electron transport system
-final electron acceptor is oxygen gas.
-total theoretical maximum number atp generated perglucose in prokaryote is 38.In eukaryotr is 36-38.This different from prokaryote because depending on how 2NADH generated in cytoplasm during glycolysis enter mitochondria resulting 2 or 3 atp per NADH but in prokaryote there are no mitochondria 38 can be produce.
metabolic pathways-
I hope I can know what species of eukaryote will produce 36 atp and 37,38.Before this I only think that plant hae specific respiration but now microbe also have respiration process that some steps similar to plants.
Carbon fixation
-light dependent reaction
consumes atp
most commo pathway is Calvin cycle.
The other name for carbon cycle is Calvin-Benson Cycle.
https://classconnection.s3.amazonaws.com/959/flashcards/1239959/gif/carbon_fixation1333280161893.gif
When learning on biology during foundation I only learn the other name for carbon fixation is calvin cycle but now I know there is one more name that is Calvin-Benson cycle.When I search I found more name about this
-Calvin-Benson-Bassham cycle
-Dark stage
Microbiological Nutrition
Photoautotroph energy source is light while carbon source is carbon dioxide
Photoheterotroph energy source is light and carbon source is organic molecules
chemoautroph energy source is inorganic molecules and carbon source is carbon dioxide
Phototrophs energy is light
When learning this I quite shock that microbes have different types of nutrient.I thought it only happen with plant.
What I have learn:
-Total maximum atp in prokaryotes is 38
-Carbon fixation is light dependent reaction
-Carbon sources for autotrophs is carbon dioxide